Additional Services
Enhancers for Your Treatment: Additional Services
There are techniques that, when combined with assisted reproduction treatments, can increase the probability of success. The use of these depends on your diagnosis.

PGTA and PGTA Plus
PGTA (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidies) and PGTA Plus are non-invasive genetic tests performed on embryos before transfer. These tests help verify that your embryos have 23 pairs of chromosomes with the expected structure.
What is the difference between PGTA and PGTA Plus?
First, it’s essential to understand that when an egg and sperm unite, they should create a cell with 23 pairs of chromosomes (a combination of DNA from both). However, there are cases where there is a gain or loss of chromosomes, and any change in the number of chromosomes raises issues with growth, development, and body system functions.
PGT-A involves taking a DNA sample from the outer layer of the embryo to examine it. While PGT-A shows the number of chromosomes and verifies that there are exactly 23 pairs (46 chromosomes), PGTA Plus provides insight into any modifications in the chromosome structure.
If structural anomalies are detected, PGTA Plus allows us to take a DNA sample from the parents or donor to determine the source of the issue. With this information, the specialist can make precise and informed decisions in the assisted reproduction process, increasing the chances of a successful IVF cycle.
PGTA or PGTA Plus is recommended if…
- You are over 35 years old
- You have had recurrent miscarriages
- You have had two or more failed IVF cycles
- There is a diagnosis of male infertility
- You previously had a baby with chromosomal abnormalities
- You have experienced repeated implantation failures
Benefits of PGTA or PGTA Plus
- Reduces miscarriage rates
- Increases pregnancy success rates per transfer
- Minimizes the number of treatment cycles needed
- Lowers the cost and time invested
Sex Selection
What is sex selection?
Sex identification is an option we offer to patients who know of a pre-existing sex-linked genetic disease in their family history to prevent its transmission.
How does it work?
Since the disease we want to avoid is sex-linked, we only need to identify the sex of the embryo before transfer. To do this, we use the DNA sample taken during PGTA or PGTA Plus and specifically analyze the chromosomes of pair 23, the sex chromosomes. If the pair is “XX,” the embryo will be female; if it is “XY,” it will be male. This allows us to select embryos for transfer that are free of risk.

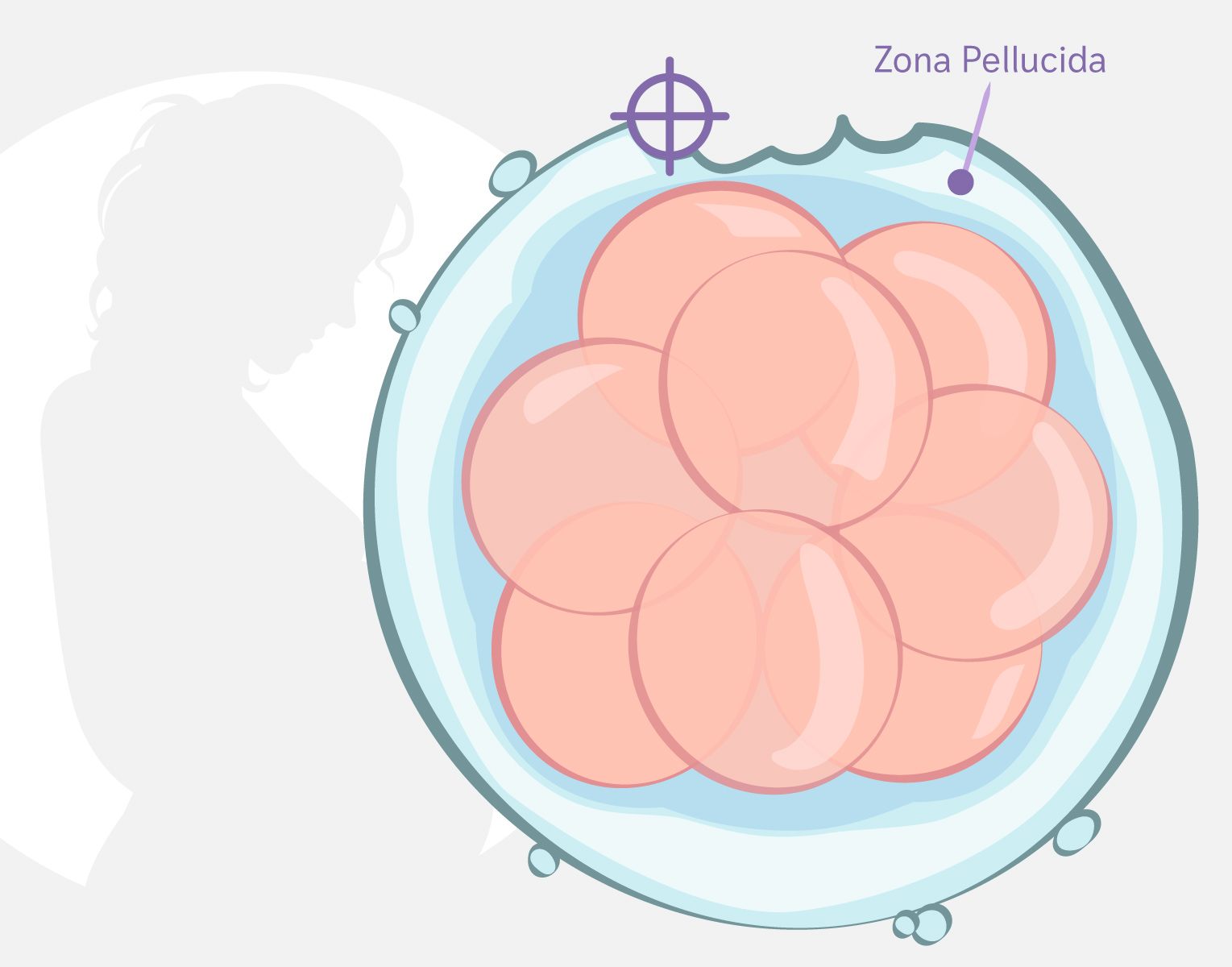
Assisted Hatching
What Assisted Hatching?
Assisted Hatching is a technique performed in the In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) lab that helps the embryo implant more easily. It involves making a small hole in the membrane surrounding the embryo, called the zona pellucida, allowing it to hatch more easily and increasing the chance of successful implantation in the uterus.
When is Assisted Hatching recommended?
- When you have had multiple transfers with good-quality embryos that did not implant
- In transfers of cryopreserved embryos
- When embryos have a thickened zona pellucida (generally in patients over 35 years old)
How is it done?
This is a safe process for the embryo, as we use a laser that allows great precision when making the openings in the zona pellucida.
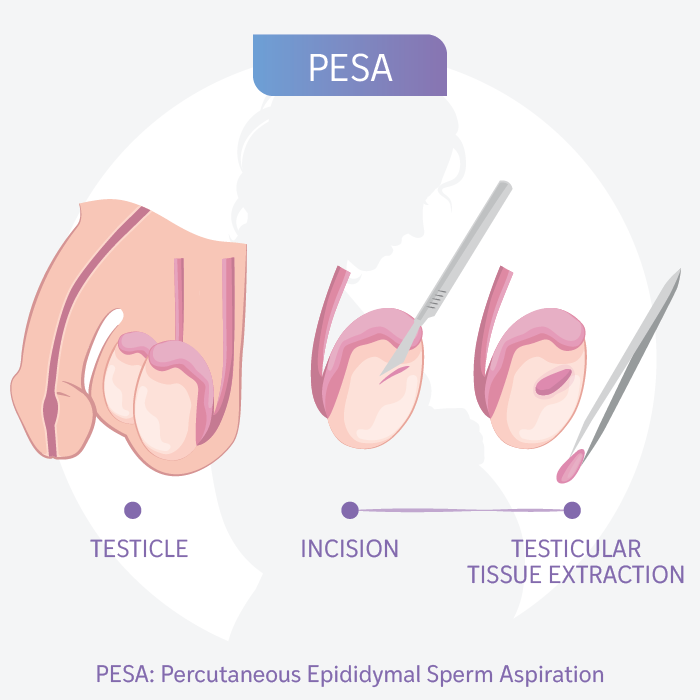
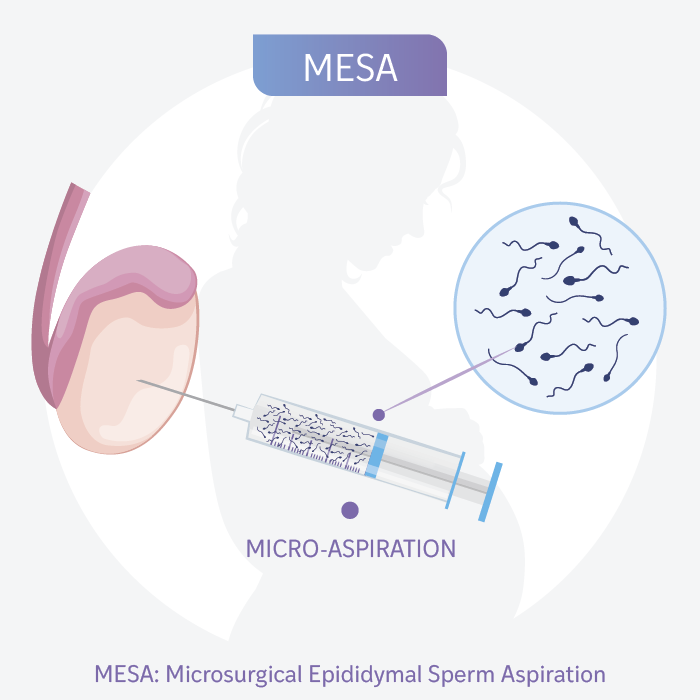
Testicular Biopsy
A technique that allows us to examine testicular tissue or obtain live sperm if there is a blockage in the seminal ducts.
What is a Testicular Biopsy?
A Testicular Biopsy is a minor surgical procedure that can be performed in two ways:
- Through a small incision in the skin, a sample of testicular tissue is taken. A suture is then used to close the wound in the testicle and another for the skin incision.
- Using a special needle to take a sample of testicular tissue. This procedure does not require a skin incision.
Choosing the right procedure will depend on your diagnosis and your doctor’s advice
When is a Testicular Biopsy recommended?
- When a semen analysis shows the absence of sperm, a concentration below 15 million sperm per milliliter, abnormal sperm shape, or significant quality issues indicating a high risk of transmitting chromosomal anomalies to embryos.
- When there is a blockage in the seminal pathway due to congenital or acquired causes.
MACS
(Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting)
What is MACS?
is a sperm selection technique that helps separate healthy sperm from dead or DNA-fragmented sperm. This method is particularly useful when sperm quality is suspected to be the cause of treatment failure.
When is MACS Recommended?
- Artificial Insemination: To enhance the quality of sperm used.
- High DNA Fragmentation: When there is a high level of DNA fragmentation in sperm.
- Recurrent Miscarriages: If there are unexplained recurrent miscarriages.
- Poor Embryo Quality: After detecting poor embryo quality and ruling out egg-related causes.
Studies have shown that this technique can improve pregnancy rates by 10-15%.
Sperm DNA Fragmentation Test
This test assesses the integrity of sperm DNA to determine if it is contributing to infertility and to guide appropriate treatment.
What is a Sperm DNA Fragmentation Test?
The Sperm DNA Fragmentation Test detects breaks in the genetic material of sperm. Such damage is associated with lower fertilization and pregnancy rates, poor embryo quality, and an increased risk of miscarriage.
Who should consider the sperm DNA fragmentation test?
This test can help couples with:
- Multiple unsuccessful IVF treatments
- Unexplained infertility
- Repeated implantation failures
- Poor embryo quality in previous cycles
- Varicocele
- Recurrent miscarriage
- Men over 45 years old
- Chronic diseases affecting sperm quality
- Smoking
- Abnormal semen analysis results